A Comprehensive Guide to Payroll Management
Payroll mistakes cost more than money. One miscalculation, one missed deadline, and suddenly you are dealing with frustrated employees, compliance headaches, and penalties that could have been avoided.
Managing payroll manually might work for a small team, but it quickly becomes unsustainable. Spreadsheets multiply, regulations shift, and the margin for error shrinks.
The solution is not working harder but smarter.
Modern payroll management can be seamless, accurate, and automated. Whether you are running a lean team of 10 or scaling to hundreds, the right approach transforms payroll from a monthly burden into a strategic advantage, one that saves hours, eliminates compliance risks, and keeps your team paid accurately and on time, every time.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how you can build a simplified payroll process, tackle common payroll challenges, and utilise automation to ease the load. Read on to discover practical tips, strategies, and top payroll software solutions that can redefine the way you handle payroll in your organisation.
Overview
Payroll management calculates employee compensation, applies statutory deductions like PF, ESI, and PT, and ensures legal compliance in India.
Payroll processing includes data collection, salary calculation, tax deductions, disbursement, and accurate record-keeping for audits.
Post-payroll tasks include generating payslips, filing compliance documents, and reconciling records to maintain accurate records.
Common challenges include complex tax regulations, compliance risks, data security, and managing payroll for distributed teams.
Automated payroll software and integrated systems streamline processing, ensure compliance, and improve efficiency using cloud, AI, and blockchain technologies.
What is Payroll Management?
Payroll management is the process of calculating and distributing employee compensation, ensuring that wages, salaries, bonuses, and deductions are processed accurately and on time. It involves complying with statutory requirements and maintaining precise records for auditing and legal purposes.
For companies in India, payroll management includes Provident Fund (PF) contributions, Employee State Insurance (ESI), professional tax (PT), and other mandatory deductions. Managing payroll correctly avoids penalties and maintains trust with employees.
Next, we explore why effective payroll management is essential for smooth operations and a satisfied workforce.
Why Payroll Management Matters for Every Organisation
Payroll management is more than just paying employees; it is a vital function that ensures accurate, timely, and legally compliant compensation. Efficient payroll processes build employee trust, prevent compliance issues, and safeguard the organisation from financial and operational risks.
Here’s how effective payroll management benefits your organisation:
Accurate Compensation: Guarantees employees receive the correct salary, allowances, and deductions in every pay cycle.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to labour laws, tax regulations, and statutory contributions like PF, ESI, and professional tax.
Time Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks, allowing HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than manual calculations.
Error Reduction: Reduces mistakes in salary computation, reporting, and statutory filings, minimising disputes and corrective actions.
Employee Satisfaction: Transparent, timely payroll strengthens trust and boosts overall workforce morale.
By prioritising payroll management, organisations can convert it from a routine task into a strategic function. Accurate, compliant, and efficient payroll processes protect against penalties, enhance employee confidence, and keep operations running smoothly.
Next, let’s understand the key stages of payroll processing and how each step contributes to accuracy, compliance, and efficiency.
What are the Stages in Payroll Processing?
Payroll processing involves several key stages that ensure employees are paid accurately and on time while meeting compliance requirements. Understanding each stage is necessary for enhancing the process and reducing errors.
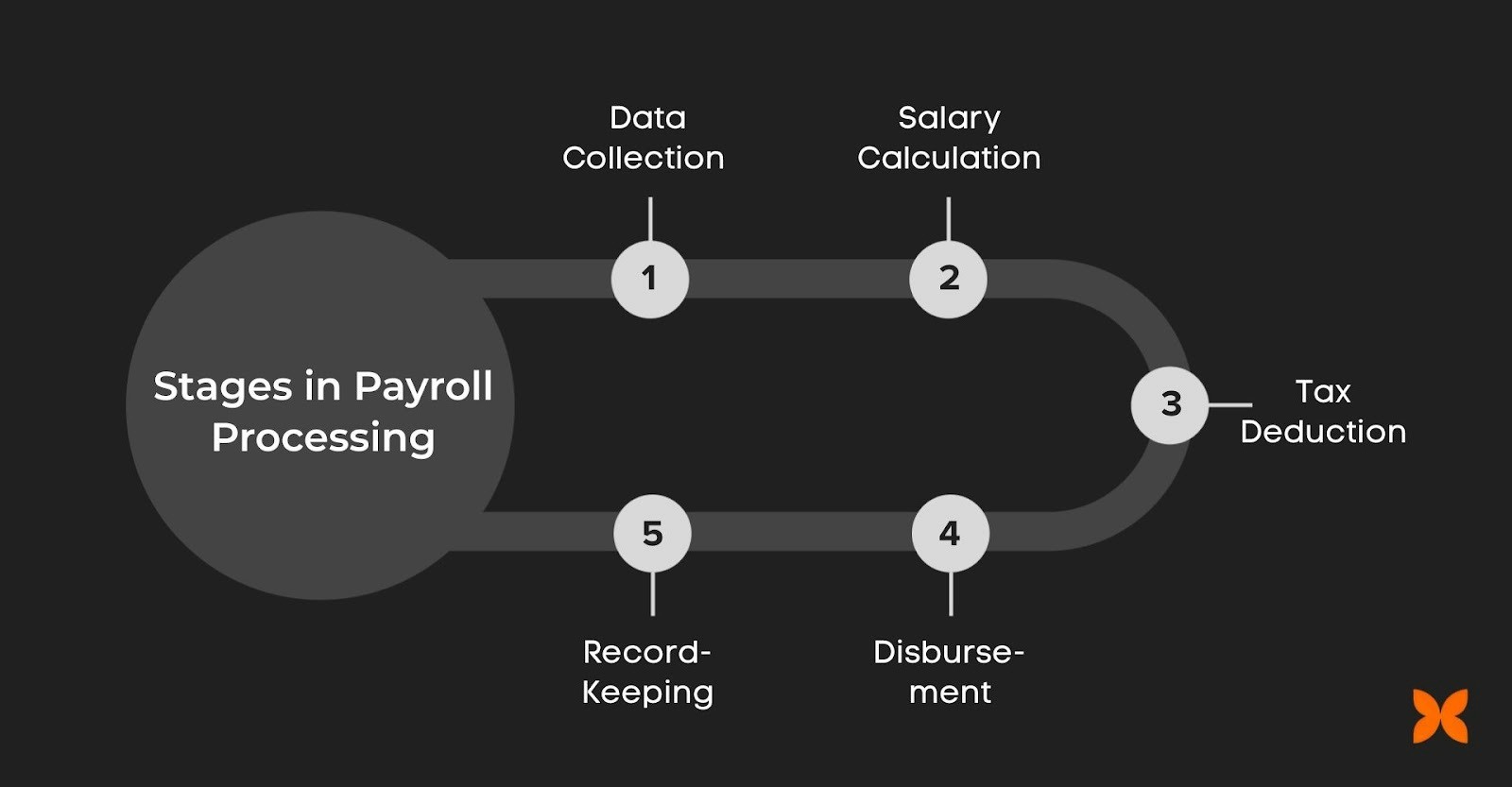
1. Data Collection
The first stage in payroll processing is gathering all the relevant data for each employee. This includes recording working hours, attendance, overtime, leave taken, and bonuses:
Timesheets: Tracking employee work hours, overtime, and flex time.
Leave Records: Accounting for any sick leave, casual leave, or vacation days taken.
Overtime: Calculating additional hours worked beyond regular shifts.
Commission or Bonuses: Including additional payments, if applicable.
Accurate data collection is crucial to ensure all compensation is correctly calculated and that discrepancies are avoided.
2. Payroll Calculation
Once all the relevant data has been collected, the next stage is salary calculation. This step involves determining the gross salary for each employee, taking into account:
Basic Salary: The fixed component of an employee’s compensation.
Allowances: Additional payments for housing, transport, or other special purposes.
Overtime Pay: Calculating overtime for employees who worked extra hours.
Incentives: Performance-based payments or commissions.
Deductions: Subtracting necessary deductions, such as income tax (TDS), Provident Fund (PF), Employee State Insurance (ESI), and professional tax (PT).
This step ensures that the total earnings for each employee are calculated correctly before tax and other deductions.
3. Statutory Deductions & Contributions
The next step is to calculate and deduct applicable taxes and statutory contributions. In India, businesses must adhere to the applicable statutory laws, which may vary from state to state, including:
TDS (Tax Deducted at Source): Employers must deduct tax from employees’ salaries based on applicable tax brackets and the individual’s taxable income.
Employee State Insurance (ESI): Both the employer and employee contribute a fixed percentage of the employee’s wages to the ESIC Scheme. For employees earning below ₹21,000 per month, ESI contributions are required to support their social security and health insurance.
Provident Fund (PF): Both the employer and employee contribute a fixed percentage of the employee’s salary to the Provident Fund, which is deposited into the employee’s PF account. This helps build a retirement corpus, providing financial security in the form of a lump sum or a pension after retirement or during specific life events.
Professional Tax (PT): Applicable in certain states, this statutory deduction is made from an employee’s wages. The amount varies by state and salary structure. For example, in Maharashtra, female employees earning up to ₹25,000 and male employees earning up to ₹7,500 are exempt from PT.
Labour Welfare Fund (LWF): A small contribution deducted from employees’ wages in certain states to fund welfare initiatives for workers, as mandated by state regulations.
Once all deductions are calculated, they are subtracted from the employee's gross salary to determine their net salary.
Read more to learn about allowances in Income Tax.
4. Disbursement
The disbursement stage is when employees receive their payments. This can be done through various methods, such as:
Bank Transfer: The most common method, where salary payments are transferred directly to the employee’s bank account.
Cheque Payments: Some organisations still use cheques, although this method is becoming less common.
Cash: In rare cases, especially in small businesses, salaries may be paid in cash.
Timely and accurate disbursement is vital for maintaining employee satisfaction, as delays in salary payments can harm morale and productivity.
5. Record-Keeping and Reporting
After payroll is processed and payments are disbursed, businesses must complete post-payroll tasks to ensure compliance, transparency, and accurate records:
Employee Payslips: Generate and distribute payslips detailing earnings, deductions, and net salary. Modern payroll platforms like Craze offer Employee Self-Service (ESS), allowing employees to view and download payslips, tax details, and investment proofs anytime.
Compliance Filing: Complete all statutory filings on time, including TDS returns, PF contributions, ESI premiums, professional tax, and other state-mandated deductions. Timely compliance helps avoid penalties.
Payroll Records & Audit: Maintain accurate payroll records for each employee, including salaries, benefits, and deductions. Conduct audits and reconciliations to ensure payments match deductions and all remittances to third parties, such as tax authorities and insurance providers, are accurate.
These steps help maintain transparency between employers and employees, ensure legal compliance, and provide a reliable reference for future audits or disputes.
Let’s now understand the key components that make up a complete payroll system, and why getting each part right is essential for smooth payroll management.
What are the Components of Payroll?
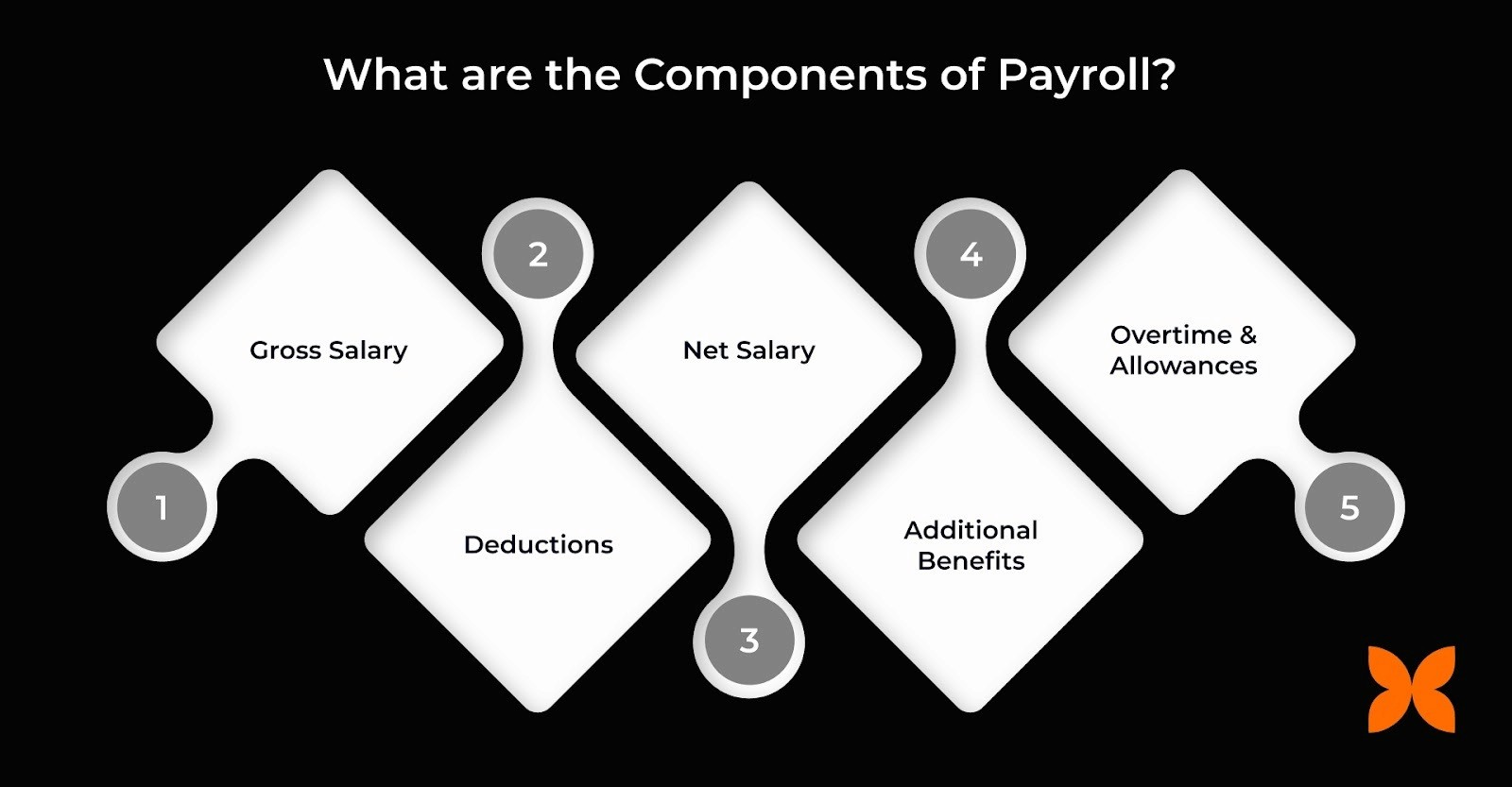
Payroll involves several key components that determine an employee’s total compensation. Understanding each part is necessary for accurate payroll management, ensuring compliance, and avoiding errors. Below is a breakdown of these components:
Component | Description |
Gross Salary | The total earnings before any deductions, including basic salary and additional allowances such as housing, transport, and special allowances. |
Deductions | Subtracted from the gross salary to determine net salary. This includes taxes, Provident Fund (PF), Employee State Insurance (ESI), and others. |
Net Salary | The final amount an employee takes home after all deductions. It represents the actual payment employees receive. |
Additional Benefits | Perks or allowances, such as bonuses, stock options, and health insurance, that may not be paid in cash but are part of total compensation. |
Overtime and Allowances | Additional pay or allowances for extra hours worked or exceptional circumstances like travel or meal allowances, calculated as per company policy. |
By effectively managing these components, businesses ensure a smooth, transparent payroll process. Next, let’s explore the different payroll processing methods and help you choose the most suitable approach for your organisation.
Read More: Understanding HR Compliance: Definition, Laws, and Best Practices
What are the Different Payroll Processing Methods?
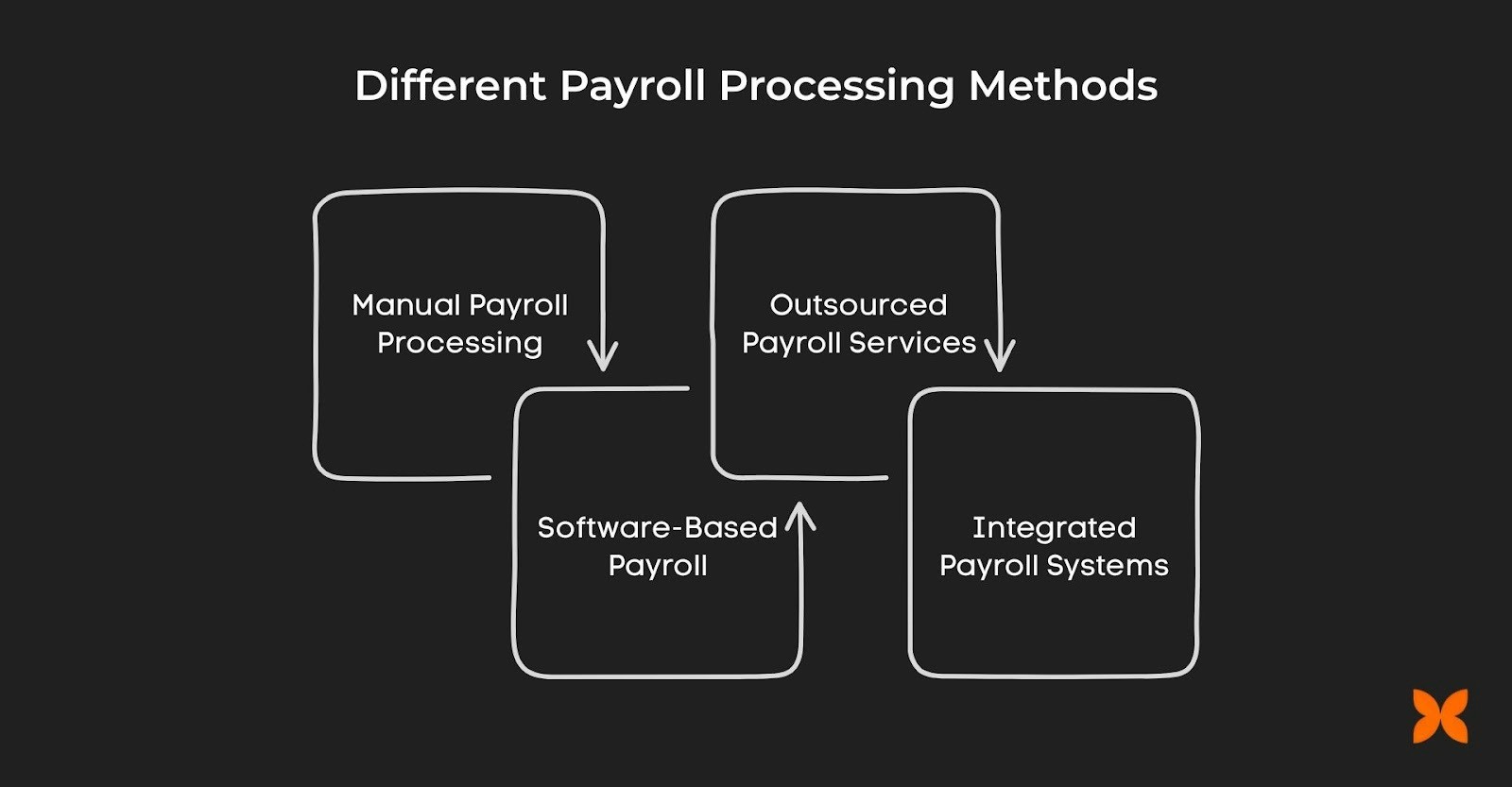
There are several ways to process payroll, each with its own set of advantages and challenges. Choosing the right payroll method depends on your organisation’s size, complexity, and resources.
Here’s a breakdown of the most common payroll processing methods:
Manual Payroll Processing
This is the traditional method where payroll is processed manually using spreadsheets or paper records. It involves calculating salaries, tax deductions, and other elements without the aid of software.
Pros: Low upfront cost, ideal for small businesses with few employees.
Cons: Time-consuming, prone to errors, and lacks scalability as the business grows.
Software-Based Payroll
Using payroll software to automate the process is a modern solution for businesses of all sizes. The software calculates salaries, applies deductions, and generates payslips automatically.
Pros: Reduces errors, saves time, ensures compliance, and can integrate with other HR systems.
Cons: Initial setup cost and learning curve for the team.
Outsourced Payroll Services
Outsourcing payroll to a third-party service provider means the company hires an external agency to handle all payroll functions, from calculation to compliance.
Pros: No need for in-house expertise, reduces administrative burden, ensures compliance.
Cons: Less control over the process, ongoing service fees.
Integrated Payroll Systems
These systems combine payroll processing with other HR functions, such as attendance, leave management, and employee data. Data is synchronised across systems, reducing manual data entry and errors.
Pros: Seamless integration, greater accuracy, reduces the need for multiple tools, and improves reporting.
Cons: Can be expensive for small businesses if not chosen correctly, may require dedicated resources for setup and maintenance.
Each payroll processing method has its own benefits, but the right choice will depend on your business’s needs and capacity. Now that we have explored payroll methods, let’s discuss the challenges businesses face in managing payroll and how to overcome them.
Challenges in Payroll Management

Managing payroll is not without its challenges, and as businesses grow, these issues can become more complex. Below are some common payroll challenges and their solutions to help you streamline the process:
Complex Tax Regulations
Keeping up with ever-changing tax laws, such as TDS, PF, and Professional Tax, can be time-consuming and error-prone.
Solution: Automate tax calculations and compliance updates with payroll software to ensure accuracy and timely filing.
Compliance Issues
Businesses must adhere to various statutory requirements, and failure to do so can result in penalties. This includes managing ESI, PF contributions, and local tax laws.
Solution: Use payroll software like Craze that automatically updates to reflect regulatory changes, ensuring compliance is always maintained.
Data Security
Handling sensitive employee information such as salary details, bank accounts, and tax data requires secure systems. Any data breaches can harm your business reputation and lead to legal consequences.
Solution: Implement robust payroll software with strong data encryption and secure access controls to protect sensitive information.
Handling Payroll for a Remote Workforce
With teams spread across multiple locations, especially internationally, managing payroll under varied tax laws and regulations can be challenging.
Solution: Cloud-based payroll systems with multi-location support can automate compliance and tax calculations regardless of employees' locations.
Employee Queries and Disputes
Payroll errors can lead to confusion, disputes, and employee dissatisfaction. Addressing these issues promptly is key to maintaining trust.
Solution: Offer employees easy access to detailed payslips and payroll records, and a transparent process for quickly resolving queries.
By identifying these challenges and implementing the right solutions, you can simplify payroll management and ensure smooth operations. Let’s now check out the best payroll software solutions available for businesses in India to help you overcome these hurdles effectively.
Best Payroll Software Solutions for Businesses in India
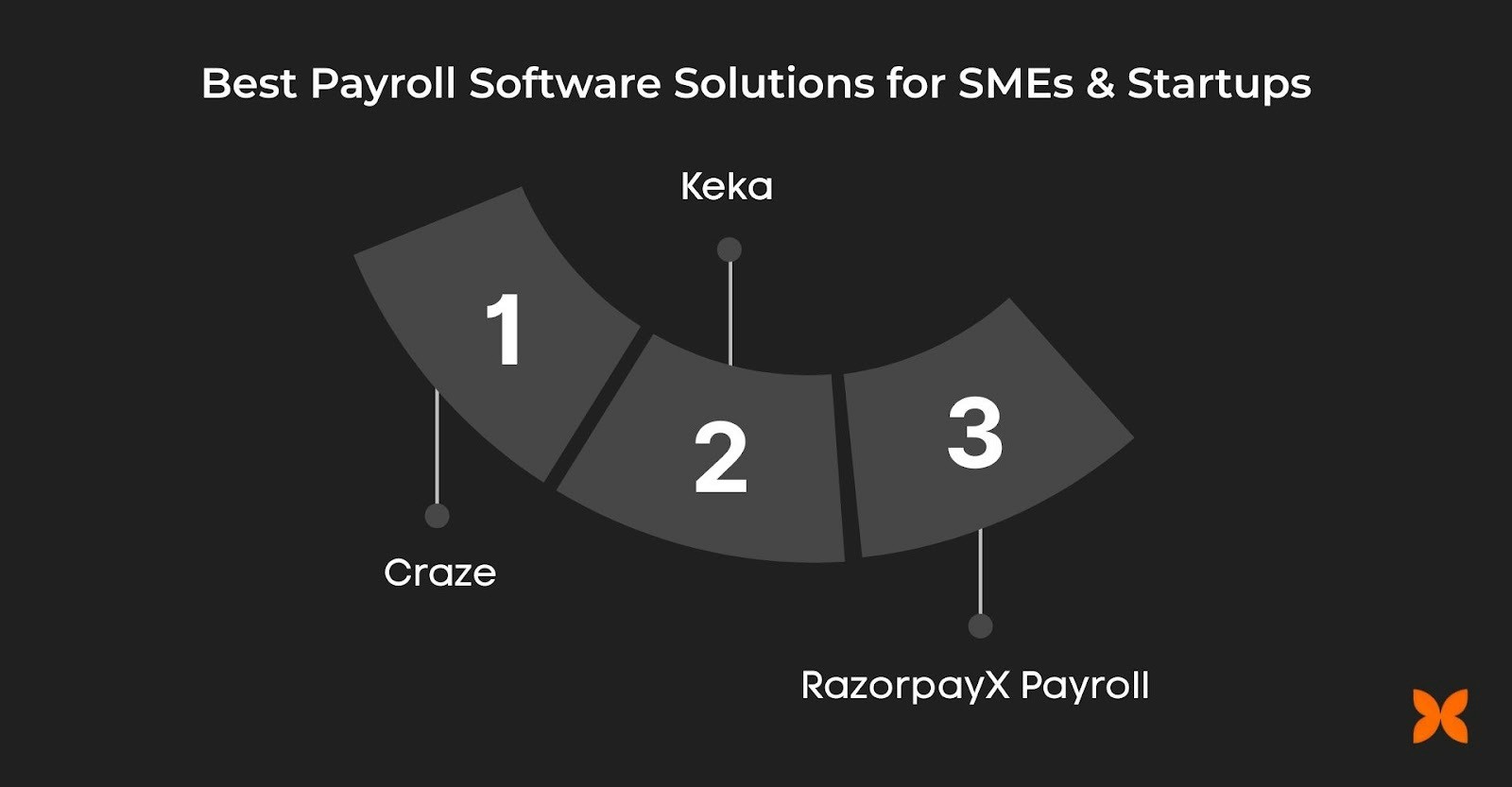
Selecting the right payroll software can simplify payroll processing, ensure compliance, and save time. Below are three of the best payroll software solutions for SMEs and startups in india.
Craze
Craze is an all-in-one solution for startups and small to mid-sized growing businesses with 50–500 employees that automates payroll, finance, HR, and IT processes. Its integrated platform helps companies stay compliant while simplifying payroll tasks and reducing administrative overhead.
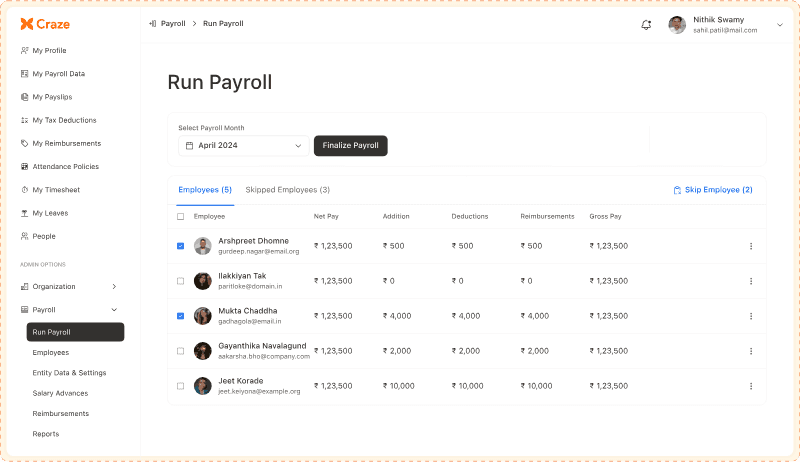
Key Features:
Automated payroll processing
Real-time statutory compliance updates (TDS, PF, ESI)
One-click salary processing
Simplified tax calculations and reporting
ESS portal for employees to view payslips & other details
Transparent, flexible pricing with no feature lock-ins
Keka
Keka is a comprehensive payroll software solution that simplifies salary management, leave, attendance, and compliance. It is well-suited for growing businesses that need a user-friendly platform to handle complex payroll operations.
Key Features:
Payroll and statutory compliance
Attendance, leave, and shift management
Recruitment and onboarding
RazorpayX Payroll
RazorpayX Payroll is an automated payroll solution designed to simplify salary processing and tax filings. It integrates seamlessly with Razorpay’s payment solutions, providing a unified platform for all financial operations.
Key Features:
Automated payroll and salary disbursement
Statutory compliance (TDS, PF, ESIC, PT)
Attendance, leave, and reimbursement management
Learn in detail about the best payroll software in India for small businesses and startups.
When choosing the right payroll software, it is essential to balance both features and pricing to ensure it aligns with your business needs. Now, let’s explore the essential statutory compliance and payroll tax requirements in India, so you can stay ahead of legal obligations and avoid costly penalties.
Statutory Compliances and Payroll Taxes in India
In India, payroll management is closely tied to statutory compliance, which involves adhering to various tax laws and labour regulations. Ensuring that your payroll process meets these legal obligations is crucial to avoid penalties and maintain smooth operations. Here's a breakdown of the key statutory requirements for businesses in India.
Act/Regulation | Applicability & Requirement |
Ensures timely and full payment of wages to employees; sets wage disbursement deadlines and restricts deductions. | |
Mandates payment of at least the government-notified minimum wage for each worker category; varies by state and sector. | |
Requires annual bonus payment (8.33%–20% of salary/wages) to eligible employees (earning ≤₹21,000/month) in establishments with ≥20 employees. | |
Mandates provident fund contributions of 12% each from the employer and employee for establishments with 20 or more employees. It applies to employees earning up to ₹15,000 per month. | |
Mandates social security and health insurance contributions for establishments with 10 or more employees (20 in some states). It applies to employees earning up to ₹21,000 per month. | |
Under the new wage code, the minimum continuous service required for fixed-term employees has been reduced from 5 years to 1 year. | |
Requires employers to deduct tax at source (TDS) from salaries as per applicable slabs and deposit with the government; file quarterly returns and issue Form 16. | |
Professional Tax (PT) Acts (State-specific) | Employers must deduct and remit professional tax where applicable, as per state laws; not all states levy PT. |
Provides for paid maternity leave (26 weeks) and related benefits for eligible women employees. |
Note: Additional labour laws and statutory acts may apply depending on the nature, size, and location of the business. Organisations should review their operations to ensure full compliance.
More Things to Consider:
Labour Welfare Fund Act: Mandatory in some states; requires periodic employer and employee contributions for employee welfare.
Shops and Establishments Act (State-specific): Regulates working hours, leave, and conditions of service for non-factory establishments; registration is mandatory in most states.
Future Trends in Payroll Management
Payroll management is evolving with advancements in technology and changing business needs. Here are the key trends businesses should prepare for:
Automation and AI: Payroll software increasingly uses automation and AI to handle tax calculations, deductions, and payroll processing, reducing errors and saving time. Key benefits of AI and automation:
Instant Payroll Processing: Automated salary calculation, tax deductions, and statutory compliance.
Automated Tax Calculation & Reporting: Real-time updates of tax slabs and automated TDS calculations.
Instant Pay Processing: Employees are paid instantly with accurate, timely deductions.
Error-Free Reporting: Payroll data and compliance reports are auto-generated and instantly synced.
Employee Self-Service Platforms: Self-service portals help employees to access their payslips, update personal information, and manage benefits, improving transparency and satisfaction.
Blockchain for Security: Blockchain technology ensures secure, transparent, and tamper-proof payroll transactions, reducing fraud and enhancing data integrity.
Real-Time Compliance and Reporting: Payroll systems are focusing on real-time compliance tracking and instant reporting to stay ahead of regulatory changes and ensure accurate filings.
Real-Time & On-Demand Pay: Employees can receive payments instantly or on demand, improving satisfaction and cash flow flexibility.
Data Analytics & Insights: Payroll systems provide actionable insights into workforce costs, trends, and optimisation opportunities.
Compliance Automation: Automatically applies changing tax laws and statutory requirements to ensure accurate filings.
Flexibility for New Work Models: Supports gig, remote, and hybrid workforce payroll with adaptable processes.
By adopting these trends, businesses can streamline payroll management, improve efficiency, and stay compliant.
Conclusion
Accurate and timely payroll is essential for businesses of all sizes, ensuring employees are paid correctly while staying fully compliant with legal requirements. It also plays a key role in maintaining trust and transparency between the organisation and its workforce.
The right systems and technology streamline operations, reduce errors, save time, and improve employee satisfaction. Modern payroll practices help organisations maintain compliance, boost efficiency, and support a motivated workforce.
FAQs
1. How do I choose the best payroll software for my company?
When choosing payroll software, consider factors like automation capabilities, compliance support, ease of use, and integration with existing systems. Ensure the software can scale with your business and offers transparent pricing. It's also crucial to evaluate the available support options.
2. What are the common payroll errors I should avoid?
Common payroll errors include incorrect tax deductions, miscalculation of overtime, failure to meet compliance requirements, and delayed payments. Regular audits, automation, and using reliable payroll software can help prevent these mistakes.
3. Can payroll software handle multiple payment methods?
Yes, payroll software like Craze, can process salaries via bank transfers, digital wallets, and other payment channels, ensuring timely, flexible payments for all employees.
4. What should I do if I face payroll compliance issues?
If you face payroll compliance issues, ensure you are up to date with the latest tax laws and statutory deductions. Automated payroll software can help you maintain compliance. You may also need to consult with a legal or tax expert to resolve any complex issues.
5. Which payroll system is best for running payroll in India?
Popular options for Indian businesses include Craze and Zoho Payroll, known for automation, compliance with local laws, and ease of use. Other widely used systems include RazorpayX Payroll and Keka HR.
