Is managing HR tasks becoming harder as your business grows and employment regulations evolve? Understanding the right features of HR software can help automate routine tasks, improve data accuracy, and enable HR teams to focus on strategic priorities.
With nearly 80% of companies now using digital HR tools for payroll, attendance, onboarding, and performance management, knowing which features to prioritise is essential.
In this blog, you’ll explore the core features of HR software that help businesses simplify HR processes, maintain compliance, and support sustainable long-term growth.
HR software automates employee management processes, reducing manual effort and errors.
It handles employee records, attendance, leave, payroll, recruitment, and performance tracking.
Core features include employee records, attendance and leave tracking, payroll management, recruitment workflows, performance appraisal, reporting, and self-service portals.
Advanced features include analytics dashboards, workflow automation, mobile access, compliance management, and integration with third-party tools.
Select HR software based on feature coverage, integration, scalability, security, and support quality.
HR software is a digital platform that centralises and automates all core human resource processes, including employee data management, payroll, attendance, recruitment, and performance tracking. It replaces manual spreadsheets and disconnected systems, providing a unified interface for HR operations.
By offering structured workflows, role-based access, and real-time reporting, HR software ensures compliance with Indian labour laws and organisational policies while supporting data-driven decision-making.
HR software enhances accuracy, efficiency, and transparency in HR operations while reducing administrative workload and operational risks. Here are a few key benefits of using HR software:
Accuracy: HR software ensures that payroll calculations, attendance records, and employee data are precise and error-free.
Efficiency: The system automates repetitive HR tasks, allowing HR teams to focus on strategic activities and employee engagement.
Compliance: HR software ensures compliance with Indian labour laws, statutory reporting requirements, and audit requirements.
Transparency: Employees can directly access payslips, leave balances, and company policies through self-service portals.
Data-Driven Insights: The platform provides analytics and dashboards that help monitor workforce performance, productivity, and attrition trends.
Scalability: HR software supports organisational growth by managing complex shift patterns, multi-location teams, and large employee bases.
Implementing HR software enables organisations to streamline HR workflows and maintain regulatory compliance. It also improves employee satisfaction, making it a critical solution for businesses with growing or challenging workforces.
Also Read: Best HR software in India to streamline your HR operations
To maximise the benefits of HR software, it’s essential to understand the key features that address both employee and organisational needs. Let's take a closer look.
HR software features define how efficiently your organisation manages payroll, attendance, leave, performance, compliance, and employee self-service. Choosing the right combination of features ensures processes run smoothly, reduces manual effort, and supports effective workforce management.
Here are 20 essential HR software features to consider for your business:
1. Employee Database Management
A centralised employee database ensures accurate, up-to-date records across HR operations. It reduces duplication, manual errors, and inconsistent employee data spread across spreadsheets or disconnected tools.
Unified Employee Profiles: Stores demographic details, job history, compensation, and statutory documents in one repository.
Version-Controlled Updates: Prevent outdated information by tracking modifications and controlling access rights.
Document Repository: Manages offer letters, contracts, ID proofs, and compliance documents with expiry tracking.
Search & Filters: Advanced filters for department, role, location, or employment type enable faster HR reporting.
Role-Based Visibility: Regulates who can view, edit, or download sensitive records, ensuring secure access.
Why It Matters: Ensures consistent, audit-ready employee data essential for payroll, compliance, and HR decision-making.
2. Recruitment & Onboarding
This feature streamlines hiring workflows by automating candidate evaluation, approvals, and onboarding tasks while maintaining complete visibility across recruitment stages.
Applicant Tracking: Centralises job postings, resumes, screening notes, and interview outcomes.
Structured Interview Workflows: Assigns interviewers, sends reminders, and standardises evaluation criteria.
Offer Letter Automation: Generates customised templates with salary details, benefits, and joining conditions.
Pre-Onboarding Tasks: Automates the collection of documents, forms, and employee declarations before Day 1.
Digital Onboarding: Provides new hires with access to systems, policies, and training tasks through checklists.
Why It Matters: Reduces hiring delays, prevents onboarding gaps, and creates a consistent joining experience for candidates.
3. Attendance Tracking
Attendance tracking ensures accurate workforce monitoring across biometric, mobile, and geo-based systems, critical for distributed, shift-driven, or field-heavy organisations in India.
Multi-Mode Attendance Capture: Supports biometric devices, QR scans, mobile apps, and web check-ins.
Geo-Fencing & Geo-Tagging: Ensures field staff clock in only from authorised work locations.
Real-Time Attendance Dashboard: Tracks present, absent, half-day, and late-ins/out in a single dashboard.
Auto-Sync With Payroll: Eliminates manual attendance corrections before payroll runs.
Exception Alerts: Flags anomalies like duplicate punches, missing punches, or policy violations.
Why It Matters: Prevents payroll errors, enhances workforce visibility, and strengthens compliance with labour regulations.
4. Leave Management
Leave management automates the entire leave lifecycle, reducing miscalculations and ensuring transparent policies across teams.
Automated Leave Requests: Employees apply digitally, and managers approve with real-time balance visibility.
Dynamic Leave Policies: Configures CL, SL, EL, leave encashment, carry-forward, and sandwich rules.
Accrual Automation: Calculates leave credits monthly or annually, per company policy.
Leave Calendar: Displays department-level leaves for workforce planning.
Payroll Integration: Automatically adjusts paid, unpaid, and LOP leaves for accurate salary processing.
Why It Matters: Reduces approval delays, ensures policy consistency, and eliminates manual tracking errors.
5. Payroll Management
Payroll management automates salary calculations, statutory deductions, and payslip generation, all of which are essential for compliance-heavy Indian payroll environments.
Automated Salary Calculations: Computes earnings, deductions, overtime, variable pay, and arrears.
Statutory Compliance Engine: Manages EPF, ESI, LWF, PT, TDS, and state-based statutory rules.
Payslip Automation: Generates itemised payslips accessible via mobile or ESS portals.
Reconciliation Tools: Detects mismatches between attendance, shifts, and pay components.
Bank File Generation: Creates bulk salary transfer files compatible with major Indian banks.
Why It Matters: Minimises payroll errors, reduces compliance risks, and delivers consistent pay cycles.
6. Performance Management
Performance management systems ensure transparent goal-setting, structured appraisals, and objective talent evaluation.
Goal & KPI Tracking: Supports OKRs, KRAs, and departmental KPIs with percentage weights.
Continuous Feedback: Enables managers and peers to provide structured feedback throughout the cycle.
360-Degree Review: Collects multi-rater evaluations for comprehensive performance insights.
Performance Analytics: Tracks trends across teams, roles, and tenure using dashboards.
Review Automation: Sends reminders, manages review cycles, and compiles appraisal scores.
Why It Matters: Enables data-driven talent decisions and reduces bias in evaluations.
7. Employee Self-Service Portal (ESS)
ESS allows employees to access HR services independently, reducing reliance on HR teams and giving them control over routine tasks.
Document Access: Provides payslips, tax statements, and company documents on demand.
Leave & Attendance Requests: Enables employees to apply for leave or correct attendance entries.
Personal Data Updates: Allows secure updates to bank details, contact information, and documents.
Service Requests: Supports IT, HR, and admin queries through ticketing workflows.
Policy Visibility: Gives employees access to company policies, handbooks, and guidelines.
Why It Matters: Improves transparency, reduces HR workload, and enhances employee experience.
8. Time Tracking
Time tracking helps organisations analyse productivity by recording hours spent on tasks, projects, and client work.
Timesheet Logging: Employees record time against tasks, projects, or clients.
Billable vs Non-Billable Tracking: Distinguishes revenue-generating work from internal activities.
Workload Analysis: Identifies over- or underutilisation through time-allocation reports.
Approval Workflows: Managers verify submitted timesheets and flag inconsistencies.
Project Costing: Estimates labour cost based on logged hours and employee rates.
Why It Matters: Supports accurate billing, project planning, and resource optimisation.
9. Benefits Administration
This feature centralises the management of insurance, reimbursements, allowances, and other company-provided benefits.
Policy Configuration: Defines eligibility criteria for insurance, allowances, or reimbursements.
Enrolment Management: Tracks employee enrolment during onboarding or policy renewals.
Benefit Usage Tracking: Monitors claims and benefit utilisation throughout the year.
Vendor Coordination: Integrates with insurers and benefit providers for real-time updates.
Cost Allocation: Maps benefit costs to departments or cost centres for financial reporting.
Why It Matters: Ensures transparency, reduces administrative effort, and helps employees understand available benefits.
10. Compliance Management
Compliance tools help organisations maintain adherence to Indian labour laws, data protection rules, and industry regulations.
Statutory Rule Engine: Automates compliance for PF, ESI, PT, TDS, gratuity, and bonus calculations.
Audit Trails: Logs all HR actions for regulatory and internal audits.
Document Compliance: Tracks expiry and renewal of licences, agreements, and mandatory documents.
Policy Enforcement: Applies company policies uniformly across leaves, attendance, and payroll.
Risk Alerts: Flags missing compliance data, incorrect filings, or policy deviations.
Why It Matters: Reduces regulatory risks and safeguards the organisation from penalties or compliance failures.
11. Document Management
HR document management systems centralise storage, retrieval, and secure handling of employee-related files, reducing fragmentation across drives, emails, and physical storage.
Structured Document Folders: Organise employee files, including contracts, ID proofs, and compliance documents.
Version Control: Tracks document updates and prevents duplication or conflicting versions.
Expiry Management: Alerts HR about document expiries, ID proofs, licences, and onboarding forms.
Access Governance: Uses permission-based controls to secure sensitive HR documentation.
Auto-Tagging: Categorises documents for faster search and compliance reporting.
Why It Matters: Ensures secure, consistent document handling and reduces audit preparation time.
12. HR Analytics & Reporting
HR analytics convert workforce data into actionable insights, supporting strategic decision-making across hiring, engagement, productivity, and cost optimisation.
Pre-Built Dashboards: Visualise headcount, attrition, attendance, payroll, and performance metrics.
Custom Report Builder: Enables HR teams to create reports tailored to business needs.
Trend Analysis: Identifies workforce patterns across tenure, departments, locations, or shifts.
Data Correlation: Links attendance, performance, and payroll data to detect operational inefficiencies.
Export & Share: Quickly exports reports for leadership reviews and compliance submissions.
Why It Matters: Strengthens HR decision-making and enables evidence-based workforce planning.
13. Training & Development
Training and development modules streamline skill tracking, learning assignments, and employee capability building across distributed teams.
Skill Matrix: Maps employee skills, certifications, and competency levels.
Learning Paths: Assigns structured training programs for specific roles or departments.
Course Tracking: Monitors completion rates and assessment outcomes.
External Training Support: Tracks participation in third-party training or certification programs.
Analytics: Measures learning effectiveness and skill progression over time.
Why It Matters: Helps organisations build a skilled workforce aligned with business requirements.
14. Shift & Roster Management
Shift and roster tools automate scheduling for multi-shift teams, ensuring coverage and compliance with work-hour regulations.
Shift Planning: Creates shift templates for daily, weekly, or monthly schedules.
Auto Assignment: Allocates shifts based on role, department, policy, and availability.
Swap Requests: Allows employees to request shift swaps with manager approval.
Attendance Integration: Syncs roster data with attendance for accurate, shift-based tracking.
Work Hour Compliance: Ensures adherence to maximum work-hour rules and break policies.
Why It Matters: Reduces scheduling conflicts and improves coverage across operations.
15. Employee Engagement Tools
Engagement tools help track employee sentiment, collect feedback, and identify areas affecting retention and productivity.
Pulse Surveys: Collects quick feedback on culture, workload, and manager effectiveness.
Engagement Analytics: Highlights engagement trends across teams, departments, or locations.
Recognition Modules: Enable peer-to-peer or manager-driven recognition.
Suggestion Boards: Allow employees to submit ideas or workplace concerns.
Action Tracking: Follows up on feedback with measurable improvement initiatives.
Why It Matters: Helps HR identify engagement gaps early and take corrective action.
16. Expense Management
Expense management digitises reimbursements and automates expense approvals, reducing manual paperwork and delays.
Digital Claim Submission: Employees upload receipts and add expense details through mobile or web.
Policy Validation: Automatically checks claims against company rules and spending limits.
Multi-Level Approvals: Routes claims through managers, finance, and HR as required.
Reimbursement Workflow: Syncs approved expenses with payroll for payout.
Audit Trails: Maintains logs for finance and compliance verification.
Why It Matters: Improves accountability and accelerates reimbursement cycles.
17. Workflow Automation
Automation tools streamline repetitive HR tasks, ensuring consistent execution of requests, approvals, and system notifications.
Rule-Based Approvals: Routes leave, attendance, payroll changes, and IT requests based on predefined rules.
Automated Notifications: Sends alerts for pending tasks, approvals, and compliance deadlines.
Cross-Module Workflows: Connects onboarding, payroll, and compliance tasks for seamless operations.
Custom Triggers: Automates actions based on events such as promotions, transfers, or exit initiation.
Reduced Manual Intervention: Minimises errors and accelerates turnaround times.
Why It Matters: Enhances operational efficiency and ensures accuracy across HR processes.
18. Integration Capabilities
Integrations enable HR software to connect with existing tools, reducing data silos and supporting end-to-end HR operations.
Payroll & Accounting Integration: Aligns financial data with Tally, QuickBooks, Zoho Books, or ERP systems.
Attendance Device Sync: Connects biometric devices and access cards for real-time punch data.
HR–IT System Links: Integrates with Active Directory, identity platforms, and provisioning tools.
API Access: Allows custom integrations with business-specific applications.
Data Consistency: Ensures uniform datasets across HR, finance, and operations tools.
Why It Matters: Prevents duplication, increases accuracy, and ensures smooth cross-system operations.
19. Security & Access Control
Security features protect sensitive HR data and enforce controlled access for different roles and functions.
Role-Based Access Control: Restricts access to specific HR modules and employee data.
Multi-Factor Authentication: Strengthens login security for HR teams and employees.
Data Encryption: Encrypts data at rest and in transit to mitigate risks.
Audit Logging: Tracks all user actions for compliance and incident investigation.
Breach Alerts: Notifies admins of unusual access attempts or data anomalies.
Why It Matters: Protects employee data, reduces breach risks, and supports compliance with data regulations.
20. Mobile Access
Mobile HR access enables employees and managers to perform essential HR tasks remotely, supporting distributed and field-heavy workforces.
Mobile Attendance: Geo-tagged punches from the mobile app for field and remote workers.
ESS Mobile Features: Leave requests, payslip downloads, and profile updates on the go.
Manager Approvals: Allows quick approvals for leave, attendance, and expenses.
Push Notifications: Ensures employees receive updates, alerts, and reminders instantly.
Secure App Access: Supports biometric app login and secure session handling.
Why It Matters: Increases accessibility for on-ground teams and ensures uninterrupted HR operations.
Also Read: Best HR Automation Tools for Businesses in India
While HR software offers many features, different business stages need to prioritise specific ones to meet their operational needs effectively.
HR requirements change as companies move from early-stage teams to multi-department operations. Each growth stage demands a specific set of HR software features that maintain accuracy, compliance, and process consistency.
The table below outlines the essential features startups, medium-sized businesses, and enterprises should prioritise based on operational needs.
HR Software Features | Startups | Medium-Sized Businesses | Enterprises |
Employee Database Management | Essential for centralising employee records | Essential with advanced fields | Essential with role-based access controls |
Attendance & Time Tracking | Basic attendance & time tracking | Advanced scheduling and shift management | Geo-fencing, multi-location support, and audit logs |
Leave Management | Basic leave request and approval workflow | Policy-based automation | Complex leave structures with compliance controls |
Payroll Processing | Simple payroll with statutory deductions | Integrations with accounting & leave-attendance modules | Multi-entity payroll, arrears, full & final settlement automation |
Onboarding & Offboarding | Digital document collection | Checklist-driven workflows | Automated provisioning, compliance-driven workflows |
Performance Management | Simple goal setting | OKRs, competency frameworks | 360-degree reviews, calibration cycles |
Expense Management | Basic reimbursement workflows | Policy-based approvals | Multi-level approvals, analytics, and audit readiness |
Document Management | Storage for essential HR documents | Version control & expiry alerts | Strict access rules, e-signatures, and compliance archiving |
Compliance & Statutory Management | Basic statutory deductions | Automated PF/ESI/PT/bonus compliance | Country-wide compliance, audit trails, risk monitoring |
HR Analytics & Dashboards | Simple reports | Productivity and trend dashboards | Predictive analytics and workforce insights |
Integrations | Must integrate with payroll | HRIS + ATS + accounting integrations | Deep ERP, CRM, and identity management integrations |
Self-Service Portal (ESS/MSS) | Basic leave and payslip access | Full ESS with updates, claims, and requests | Customised workflows, multi-level approvals |
Shift & Roster Management | Optional | Important for multi-team operations | Highly advanced with forecasting |
Recruitment & ATS | Optional/minimal ATS | Structured hiring workflows | Enterprise-grade ATS with automation and assessments |
Learning & Development | Optional | Basic LMS | Enterprise-grade LMS with certifications & career paths |
Aligning HR software features with your business stage ensures the system supports current workflows while remaining scalable. This structured approach enables better control over data, compliance, and workforce processes, allowing companies to adopt the right capabilities at the right time.
Also Read: Best Payroll Software in India for Small Businesses and Startups
With the key HR software features clarified, the next step is understanding how to choose the right provider.
Selecting the right HR software provider keeps HR processes efficient, accurate, and compliant as your business grows. The wrong choice can cause integration problems, limit scalability, and reduce support quality. Evaluating providers based on your business needs ensures a solution that aligns with operational priorities, workforce size, and growth plans.
Here are a few key factors to consider when selecting the right HR software provider:
Feature Coverage: The provider must include HR software features tailored to your business stage, including payroll, attendance, leave, and performance management. Optional modules like recruitment, learning, and expense management help prevent gaps as the business grows.
Integration Capabilities: Compatibility with existing systems, such as payroll, accounting, ERP, and time tracking, is essential. The provider should offer APIs or ready-made connectors to reduce manual data entry and ensure seamless workflows.
Compliance and Data Security: The provider must comply with Indian labour laws, tax regulations, and statutory reporting requirements. Robust data encryption, access control, and audit trails are necessary to protect sensitive employee information.
Scalability and Customisation: The platform should scale as your workforce grows or expands across locations. It should also allow you to customise workflows, policies, and reports to match your organisation’s processes.
Vendor Support and Reliability: Strong customer support, clear service-level agreements, and reliable onboarding processes are crucial. Client testimonials and case studies can help verify the provider’s real-world reliability and responsiveness.
Cost and ROI: Analyse the total cost of ownership, including subscription fees, implementation, and ongoing maintenance. Consider the long-term value in terms of efficiency gains, reduced errors, and assurance of compliance.
Choosing the right HR software provider requires balancing features, integration, compliance, scalability, cost, and support to optimise HR processes and drive sustainable growth.
After evaluating key factors for selecting HR software, it is essential to see how a platform like Craze addresses these requirements in practice.
Craze is an integrated people operating system that brings HR, payroll, attendance, compliance, and performance into one platform. All modules stay in real-time sync, so teams do not spend payroll week reconciling data across multiple tools.
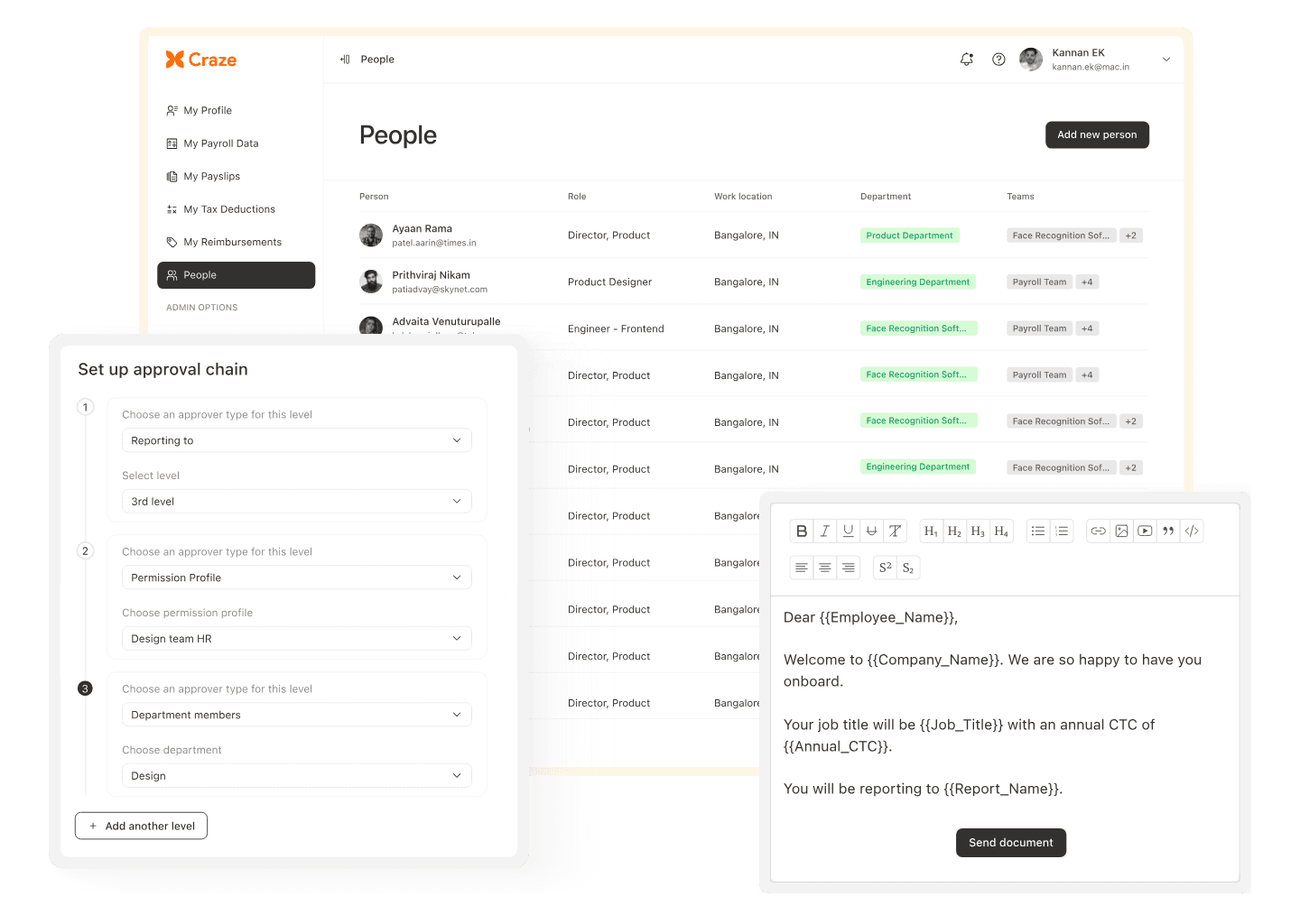
Based on the provider selection checklist above, including feature coverage, integrations, compliance, scalability, and support, here is how Craze performs in practice:
Real-time sync across HR, attendance, leave, and payroll so updates reflect instantly and reduce manual reconciliation work.
India-ready payroll and compliance workflows covering PF, ESI, PT, TDS, and statutory documents, helping organisations minimise compliance risk and maintain consistent pay cycles.
Employee and manager self-service for payslips, leave requests, attendance corrections, approvals, and document access, reducing dependency on HR for routine queries.
Workflow automation with full audit trails across approvals and critical HR actions, ensuring consistency and audit readiness.
Optional IT and asset management workflows for equipment requests, assignment, and offboarding, making onboarding and exits smoother without needing a separate system.
Best suited for: Indian businesses with 50 to 500 employees that want a single system for HR, payroll, and attendance, with fewer errors, lower administrative effort, and faster monthly closures.

1. How can HR software improve compliance beyond statutory requirements in India?
Modern HR software tracks internal company policies, audit trails, and automated approvals in addition to statutory regulations. This reduces human errors, ensures timely reporting, and provides documentation for internal audits, helping Indian businesses maintain operational discipline alongside legal compliance.
2. Can HR software help optimise workforce costs without reducing headcount?
Yes. Features like time tracking, shift management, and analytics identify underutilised resources, overtime trends, and productivity gaps. By redistributing workloads, automating approvals, and aligning schedules, companies can reduce unnecessary expenses while keeping staff intact.
3. How does HR software support hybrid and remote work models in Indian companies?
Mobile access, geo-tagged attendance, and self-service portals allow employees to clock in, submit requests, and access payslips remotely. Managers can approve leaves, monitor time, and track productivity from any location, ensuring seamless operations across office, remote, and field teams.
4. Is HR software useful for startups with fewer than 50 employees?
Absolutely. Even small teams benefit from centralised employee records, digital leave management, payroll automation, and compliance tools. This prevents manual errors, saves administrative time, and lays a scalable foundation for growth as the organisation expands.
5. How does workflow automation in HR software reduce operational risk?
Automated workflows enforce consistent processes, eliminate manual errors, and provide audit trails for approvals, payroll, and document management. Indian companies can maintain compliance, track responsibilities, and mitigate risks associated with missed deadlines or inconsistent policy enforcement.
