Day-to-day HR work shouldn’t feel like a maze of spreadsheets, late nights fixing payroll errors, or chasing compliance deadlines that never stop shifting. Yet for many Indian companies still managing attendance, pay runs, and leave tracking manually, this is the reality: constant firefighting instead of strategic people management. That’s where modern HR software changes the game.
Organisations that automate core HR processes reduce repetitive work, cut mistakes, and get real-time visibility into their workforce. In fact, a recent industry snapshot shows that over 59% of enterprises in India have adopted HR software in the past year, and only 7% remain without such systems today, signalling widespread digital uptake across sectors.
In this blog, we will explore the HR system benefits you can realistically expect, with examples you can visualise and apply.
HR software replaces spreadsheet-driven HR processes with structured systems for payroll, compliance, and workforce management.
Core HR system benefits include faster payroll processing, improved statutory accuracy, and fewer manual approvals.
Indian organisations gain from features that support multi-entity payroll, contractors, and region-specific compliance.
Automating onboarding, attendance, reimbursements, and assets reduces delays and operational risk.
Monitoring KPIs like payroll cycle time and compliance errors helps validate ROI and efficiency gains.
As organisations grow, HR complexity does not increase in a straight line. Each new hire, contractor, or legal entity multiplies approvals, payroll rules, compliance checks, and data dependencies. What worked at 30 employees starts breaking at 100, and becomes risky at 300.
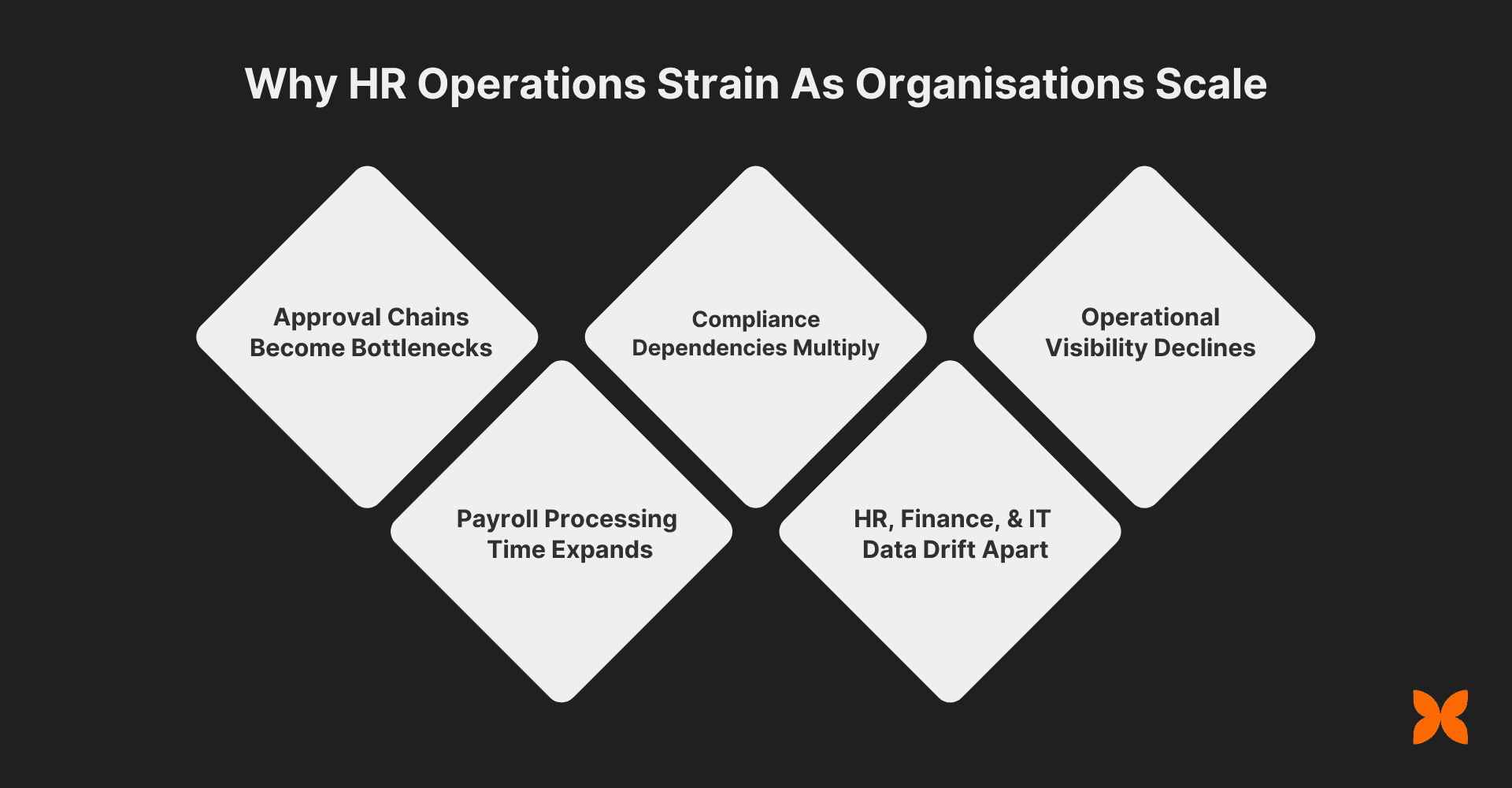
Below are the structural reasons HR operations begin to strain as scale increases:
Approval Chains Become Bottlenecks: Leave, reimbursement, and payroll approvals move across managers, finance teams, and HR. Without systemised workflows, files wait in inboxes, decisions stall, and payroll cut-off dates are missed.
Payroll Processing Time Expands Disproportionately: Adding contractors, interns, or a second entity introduces different pay structures, deduction rules, and payout methods. Payroll that once took hours can stretch into multiple days each cycle.
Compliance Dependencies Multiply: As headcount grows across locations, statutory tracking requires synchronising attendance, payroll data, and filings. Manual reconciliation increases the risk of late submissions or incorrect reporting.
HR, Finance, and IT Data Drift Apart: Employee changes are rarely reflected simultaneously across HR records, payroll sheets, and asset logs, creating inconsistencies that surface during audits or exits.
Also read: 10 Best HR Software in India For Your Growing Business
As these challenges add up, organisations turn to structured tools to regain control, making the HR system benefits of modern HR software increasingly evident.
HR software addresses specific operational breakdowns that emerge as organisations scale. Each benefit below is tied to a real HR, payroll, or compliance challenge and the system capability required to fix it. This section focuses on practical outcomes, not theory.
Below are the key benefits of using HR software in day-to-day HR operations:
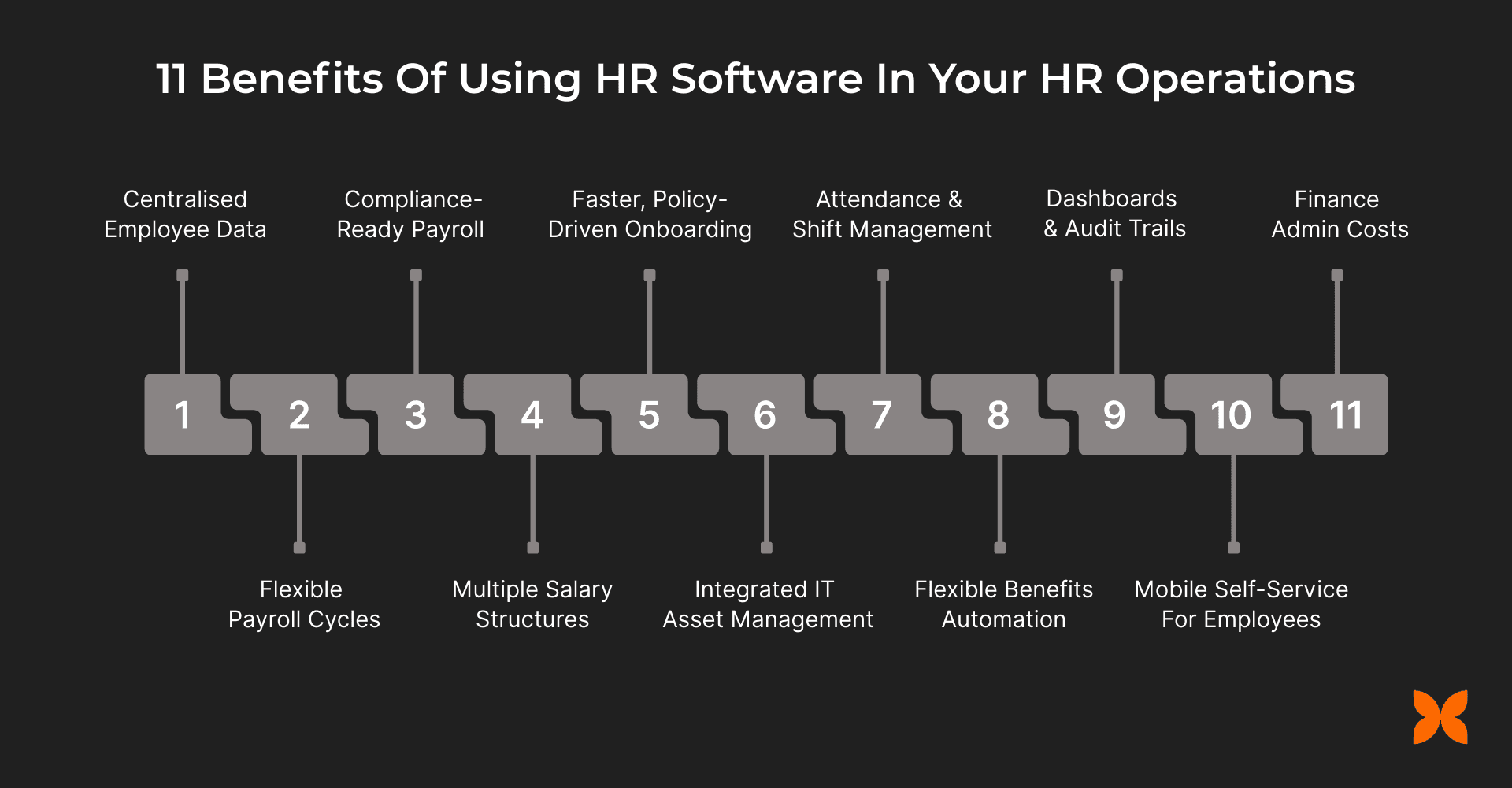
1. Centralised Employee Data and A Single Source Of Truth
As teams grow, employee information spreads across offer letters, payroll sheets, attendance logs, and asset trackers. Centralising this data ensures every function works from the same, current information, reducing dependency on manual cross-checks and follow-ups.
Below are the operational advantages of centralised employee data:
Unified Employee Master Records: Personal details, role history, compensation, and employment status are maintained in one profile, eliminating discrepancies across departments.
Version-Controlled Document Management: Offer letters, contracts, and policy acknowledgements are stored with revision history, ensuring teams reference the latest approved documents during audits or disputes.
Complete Employee Lifecycle Visibility: Every change, from onboarding and role transitions to exits, is logged chronologically, allowing HR and leadership to track workforce movements accurately.
Faster Audit and Verification Processes: Consolidated records reduce the time required to validate employee data for statutory checks, internal reviews, or due diligence exercises.
2. Payroll Automation With Flexible Payroll Cycles
Payroll complexity increases when organisations operate different pay schedules, manage multiple entities, or process contractor payments alongside regular salaries. Automating payroll with flexible cycles ensures accuracy and predictability, even when pay structures and timelines vary across teams or business units.
Below are the practical payroll automation capabilities that address these challenges:
Configurable Payroll Cycles: Payroll can be run weekly, bi-weekly, monthly, or on custom cycles, allowing organisations to align payouts with employment terms and operational needs.
Multi-Entity Payroll Processing: Separate legal entities can be configured within the same system, enabling independent payroll runs while maintaining consolidated oversight for finance teams.
Downloadable Bank Advice Files: For organisations following traditional payment methods, system-generated bank advice files ensure payout accuracy without manual data preparation.
Pre-Go-Live Payroll Validation: Payroll cycles are mapped during setup and validated through sample runs, helping teams identify discrepancies before the first live payout.
For example, platforms like Craze support flexible payroll cycles, multi-entity processing, and direct payouts from a central dashboard, reducing manual effort and payroll errors.
3. Compliance-Ready Payroll & Local Statutory Reporting
Payroll compliance in India goes beyond salary calculations. HR teams must track deductions, generate statutory reports, and meet filing timelines across multiple laws.
Below are the compliance capabilities that support statutory accuracy:
Automated Statutory Deductions: Payroll calculations account for applicable TDS, PF, and ESI deductions based on employee eligibility and salary structure, ensuring consistency across pay cycles.
Built-In Statutory Report Generation: Mandatory reports such as Form 16, PF summaries, and ESI statements can be generated directly from payroll data without separate compilation.
State and Threshold Awareness: Statutory applicability is tracked based on employee location, wage limits, and organisational setup, reducing the risk of applying uniform rules where variations exist.
Compliance Validation During Payroll Setup: Statutory configurations are reviewed and validated during implementation to ensure alignment with current regulations, with the understanding that rules may vary by state and organisation size.
4. Multiple Salary Structures & Contractor Payments
As organisations diversify roles and engagement models, a single salary format becomes impractical. Managing full-time employees, interns, and contractors requires different compensation logic, payout schedules, and reporting formats.
Below are the operational capabilities that support varied workforce compensation:
Role-Based Salary Templates: Distinct salary structures can be created and assigned by team, role, or entity, ensuring compensation components align with employment terms.
Entity-Specific Compensation Mapping: Salary configurations can differ across legal entities, allowing finance teams to maintain accurate cost allocation and statutory treatment.
Contractor Invoice and Payment Records: System-generated contractor reports provide clear visibility into payouts, billing cycles, and outstanding liabilities for finance reconciliation.
Consistent Compensation Governance: Structured templates reduce discretionary changes, helping organisations maintain internal parity and audit clarity across workforce categories.
5. Faster, Policy-Driven Onboarding and Offboarding
Onboarding and exits often fail due to missed steps, delayed approvals, or unclear ownership. Standardising these processes through policy-driven workflows ensures every task is executed in sequence, reducing dependency on manual coordination and individual follow-ups across HR, IT, and finance teams.
Below are the operational components that enable structured onboarding and offboarding:
Digital Offer and Contract Execution: Offer letters and employment agreements are shared digitally for review and signature, ensuring documentation is completed before the joining date.
Automated Onboarding Checklists: Role-based checklists trigger tasks such as documentation collection, system access setup, and payroll inclusion without manual tracking.
Probation and Confirmation Tracking: Probation timelines and review milestones are system-defined, preventing missed confirmations or delayed role updates.
Equipment Issuance and Recovery Workflows: Device allocation at onboarding and asset return at exit are embedded into the employee lifecycle, reducing loss and follow-up gaps.
6. Integrated IT Asset Management and Access Revocation
As teams adopt hybrid work and issue more devices, tracking assets manually increases the risk of loss, security gaps, and compliance issues. Integrating asset management with HR workflows ensures equipment and system access follow the employee lifecycle without relying on manual coordination.
Below are the operational capabilities that enable controlled asset and access management:
Centralised Asset Inventory: All hardware and tools are logged in a single repository with ownership, status, and assignment history mapped to employees.
Employee-Linked Asset Assignment: Devices can be issued directly from an employee profile, ensuring clear accountability from the first day of allocation.
Automated Access Revocation At Exit: Offboarding events trigger access removal through connected identity systems once assets are marked as returned.
Payroll-Linked Asset Deductions: Optional payroll adjustments can be applied for recoveries or deductions, keeping financial records aligned with asset status.
Craze automatically tracks, issues, and recovers all company devices by linking asset management to HR workflows. Ensure no device is lost, approvals are followed, and new hires are productive from day one.
7. Leave, Attendance, and Shift Management With Policy Controls
Tracking attendance and leave becomes operationally complex when teams work across locations, time zones, or rotating shifts. Relying on manual logs or informal approvals increases discrepancies and payroll corrections.
Below are the operational controls that support reliable time and leave management:
Geo and Time-Based Attendance Capture: Attendance punches are recorded based on defined locations and time rules, improving accuracy for remote and field-based teams.
Shift and Roster Configuration: Rotational shifts and variable work schedules are mapped in advance, enabling predictable attendance and payroll alignment.
Custom Leave Policy Frameworks: Leave rules are configured by role, location, or employment type, ensuring consistent application across teams.
Automated Leave Accruals: Leave balances accrue automatically based on policy definitions, removing manual calculations and periodic reconciliations.
8. Reimbursements, Advances, and Flexible Benefits Automation
Manual handling of reimbursements and salary advances often leads to approval delays, inconsistent policy application, and accounting mismatches. Automating these workflows ensures requests follow defined rules, approvals happen on time, and financial records stay aligned with payroll and accounting systems.
Below are the operational mechanisms that enable controlled reimbursement and benefits management:
Configurable Reimbursement Policies: Expense categories, limits, and eligibility rules are predefined to ensure consistent policy enforcement across teams.
Structured Loan and Salary Advance Workflows: Employee loans and advances follow documented approval, repayment, and deduction schedules without ad hoc handling.
Payroll-Integrated Recoveries: Approved advances and recoveries are reflected directly in payroll calculations, preventing separate tracking or reconciliation.
Accounting-Ready Expense Records: Reimbursement data is formatted for seamless transfer to accounting systems, supporting accurate expense classification and audits.
9. Strong Reporting, Dashboards, and Audit Trails
As workforce size and payroll volume increase, decision-making depends on accurate, timely data rather than static spreadsheets. Centralised reporting within HR software enables finance and leadership teams to analyse costs, validate compliance, and respond to audits without reconstructing data from multiple sources.
Below are the reporting and visibility capabilities that support informed decisions:
Comprehensive Payroll and CTC Reports: Master CTC summaries and monthly salary registers provide clear visibility into compensation costs across roles, teams, and entities.
Contractor Invoice and Payment Reports: Detailed contractor statements support payment tracking, cost allocation, and reconciliation with finance records.
Built-In Compliance Reporting: Statutory reports are generated from payroll data, reducing manual compilation and improving audit preparedness.
Accounting System Export Capability: Payroll and expense data can be exported in structured formats compatible with accounting tools, enabling accurate forecasting and headcount cost planning.
10. Mobile Self-Service For Employees and Managers
As teams become more distributed, HR processes that rely on desktop access or email approvals slow down decision-making. Mobile self-service enables employees and managers to complete routine actions in real time.
Below are the mobile-enabled capabilities that streamline daily HR interactions:
On-The-Go Request and Approval Management: Leave, reimbursement, and attendance requests can be submitted and approved directly from mobile devices, preventing delays due to unavailability.
Instant Access To Payroll Information: Employees can securely view payslips, tax documents, and salary details without raising support tickets.
Digital Document Review and Signing: Employment-related documents can be reviewed and signed on mobile, ensuring timelines are met without in-person dependencies.
Reduced HR Support Interventions: Self-service access lowers routine HR queries, allowing HR teams to focus on workforce planning and governance.
11. Reduced HR & Finance Admin Costs With Measurable ROI
As payroll volumes and compliance responsibilities grow, administrative effort increases faster than headcount. Without automation, HR and finance teams spend a disproportionate amount of time on repetitive validation and corrections.
Below are the costs and ROI drivers that organisations can track post-implementation:
Payroll Processing Time Reduction: Automated calculations and approvals reduce the hours spent per payroll cycle, especially for multi-entity or mixed workforce payrolls.
Lower Error Correction Effort: System-driven rules minimise rework caused by incorrect attendance data, deduction mismatches, or manual overrides.
Transparent ROI Measurement Framework: Cost savings can be estimated using a simple model: hours saved per cycle multiplied by the average hourly cost of HR and finance resources.
Data-Backed Budget and Workforce Planning: Consistent cost visibility enables leadership to forecast hiring impact and administrative overhead with greater accuracy.
Also read: 10 Best Time Tracking Software for Efficient Team Management
Move from spreadsheets to a structured HR system effortlessly with Craze. Consolidate employee data, map policies, and automate approvals in one platform built for growing Indian businesses.
Now, the focus shifts to choosing a platform that consistently delivers these HR system benefits for growing Indian businesses.
Growing organisations need systems that reduce operational friction without introducing enterprise-level complexity. Craze is built for Indian businesses that want to realise the full HR system benefits discussed above without fragmented tools or manual workarounds.
Unified HR, Payroll, and IT System
Craze brings employee data, payroll processing, and IT asset management into one connected platform, enabling a single source of truth across the employee lifecycle.Workflow-Driven Operations Across the Employee Lifecycle
Core processes such as onboarding, payroll runs, reimbursements, approvals, exits, and full-and-final settlements run as structured workflows, reducing delays and manual coordination.Flexible Payroll With Built-In Compliance
Craze supports multiple payroll cycles, legal entities, salary structures, and contractor payments, while generating statutory reports for TDS, PF, ESIC, and Form 16 directly from payroll data.Finance-Ready and India-Focused by Design
Payroll and expense data integrate cleanly with accounting systems, while compliance logic aligns with Indian statutory requirements, enabling scale without operational risk.

With the right system in place, these HR system benefits come together to support sustainable growth.
As organisations scale, HR operations stop being purely administrative and start influencing compliance outcomes, cost control, and workforce productivity. Understanding the benefits of the HR system helps you move away from fragmented processes toward structured, auditable, and predictable people operations that can support long-term growth.
Craze brings these benefits together in a single, modern HR, Payroll, and IT system built for Indian businesses. By combining automated workflows, flexible payroll configurations, compliance-ready reporting, and integrated asset management, Craze enables growing teams to manage complexity without increasing operational overhead.

1. What is the difference between HR software and HRMS?
HR software typically focuses on core administrative functions like employee records, attendance, and payroll. HRMS is a broader category that may include talent management, performance reviews, learning, and analytics. Many modern platforms combine HR and HRMS capabilities into one integrated system.
2. Is HR software mandatory for Indian companies by law?
Indian labour laws do not mandate HR software specifically. However, businesses are legally required to maintain accurate payroll records, statutory filings, and employee documentation. HR software helps organisations meet these obligations consistently and reduces the risk of non-compliance due to manual errors.
3. How long does it take to implement an HR system in a mid-sized company?
Implementation timelines vary based on data readiness and process complexity. For most mid-sized organisations, core HR and payroll setup can be completed within a few weeks, including data migration, payroll validation, and basic user training.
4. Can HR software work for companies with fewer than 100 employees?
Yes. HR software is increasingly used by startups and smaller teams to establish structured processes early. It helps avoid future rework by setting up scalable payroll, attendance, and compliance systems before operational complexity increases.
5. What are the common signs that Excel-based HR management is no longer sustainable?
Frequent payroll corrections, delayed approvals, compliance anxiety, and reliance on a single HR resource are common indicators. When basic HR tasks consume disproportionate time or create recurring errors, spreadsheets usually stop being practical.
