Cryptography Policy: Meaning, Importance +Free Sample Template
Understand cryptography policy key components, compliance needs, and implementation steps. Get a free, editable sample template for your business. Read more.
Share
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A cryptography policy is the mandatory, documented rulebook that ensures all sensitive company data is encrypted, making it unreadable to unauthorised parties even if a breach occurs.
This policy is essential for mitigating financial risk and ensuring regulatory compliance, standardising security controls across all data assets.
The policy must clearly mandate approved standards (AES-256/RSA-2048), detail the secure handling of key management (generation, storage, rotation), and assign specific roles and responsibilities.
Successful deployment requires a phased approach: conducting a risk assessment, forming a cross-functional steering group, integrating secure technology solutions, and defining clear compliance metrics.
A free, editable policy template is available for immediate download to help your organisation establish cryptographic standards and secure its data without delay.
A cryptography policy is your company’s documented rulebook for how every piece of sensitive data must be protected using codes and cyphers. Its core purpose is to ensure all confidential information is encrypted or scrambled so that even if a threat actor gains unauthorised access, the data remains unreadable and useless to them.
This policy establishes a single, clear, company-wide standard, removing the risk that employees or departments might use weak or inconsistent security methods. It acts as a mandatory control to protect valuable business assets and maintain the confidentiality and trustworthiness of the data you handle.
With a clear understanding of what this policy is, we can now look at why it's vital for your business.
Also Read: Employee Database Management System for HR Leaders: What It Is, How It Helps, and How to Choose
Every business, regardless of size, deals with sensitive information, from employee payroll to customer payment details. A formal cryptography policy is your commitment to turning that data into an asset rather than a liability, protecting your company's financial and legal standing.
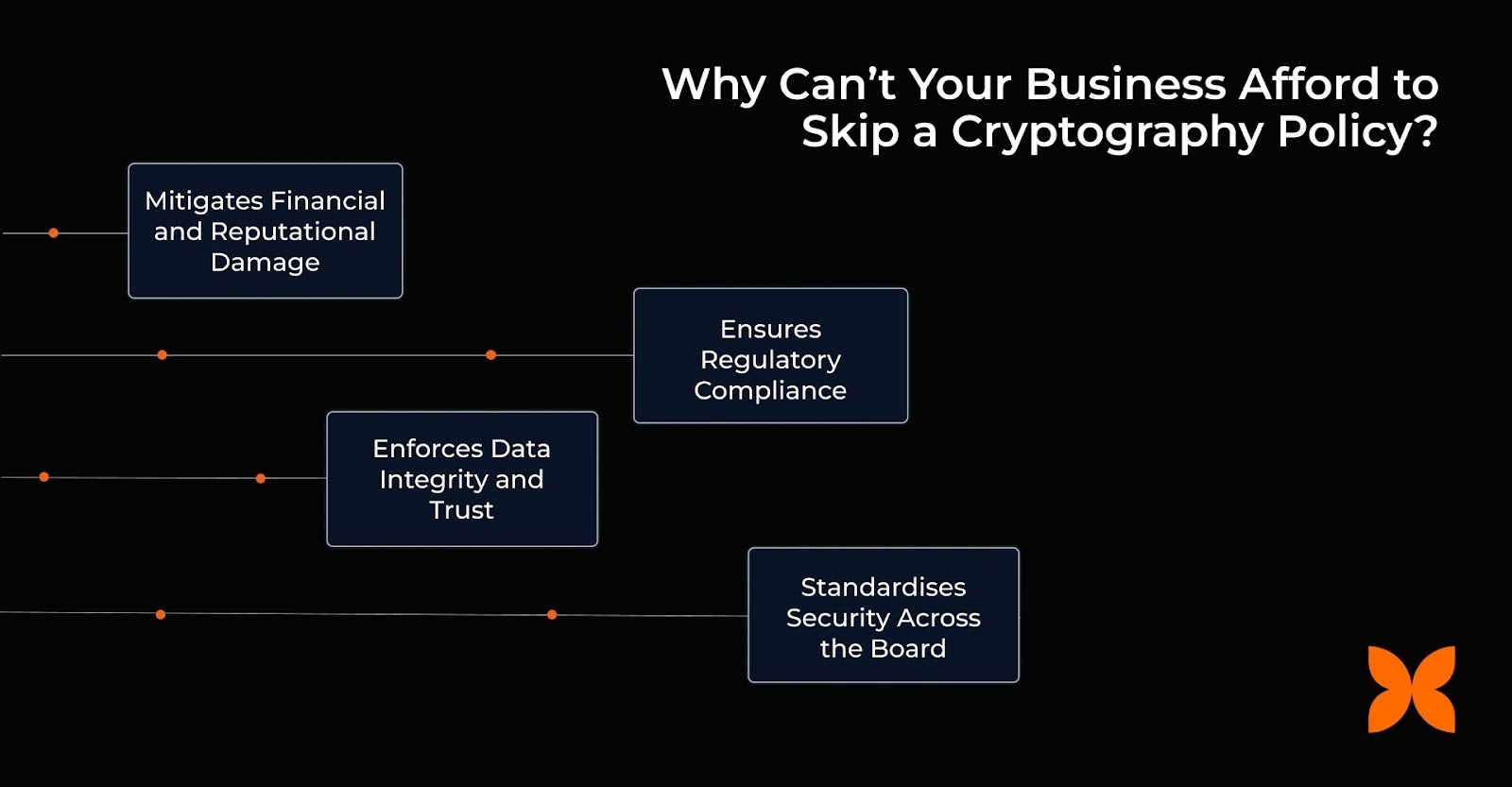
Here are the core benefits this policy delivers to your business:
Mitigates Financial and Reputational Damage: Encryption makes stolen data useless to attackers, directly reducing the chances of a catastrophic breach that leads to millions in losses, operational downtime, and public backlash.
Ensures Regulatory Compliance: The policy mandates adherence to data protection laws, like India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP), avoiding penalties that can run into crores of rupees for non-compliance.
Enforces Data Integrity and Trust: By defining strict standards for secure hashing and digital signatures, the policy guarantees that the data your business relies on hasn't been secretly altered, which is crucial for financial transactions and audit trails.
Standardises Security Across the Board: It eliminates scattered, inconsistent encryption efforts by providing a single set of rules for approved algorithms and secure key management, ensuring all sensitive assets are protected uniformly.
To put this protection into action, we need to know exactly what elements make up an effective policy.
Also Read: HR Records Management: The Ultimate Business Guide
To ensure your policy delivers comprehensive protection and meets legal mandates, especially with Indian data laws, it must clearly define the technical and procedural requirements.
A strong policy is built upon these essential pillars:
Approved Cryptographic Standards: Clearly define which encryption algorithms (like AES-256 and RSA-2048) and hashing functions (like SHA-256) are mandatory for all business data, ensuring consistent security strength.
Secure Key Management: Detail the procedures for the entire lifecycle of cryptographic keys: how they are generated, how they are securely stored (e.g., in a Hardware Security Module or vault), how often they must be rotated (changed), and how they are safely retired.
Data Encryption Mandates: Specify rules for protecting data in all states, including Data at Rest (stored on servers, backups, and hard drives) and Data in Transit (data moving across networks, typically via protocols like TLS/SSL).
Acceptable Use and Access Control: Outline which roles or systems are authorised to use specific cryptographic tools and how access to the decrypted data is strictly controlled and monitored.
Compliance and Governance: Define the specific legal and regulatory requirements (e.g., India's DPDP Act, GDPR if applicable) that the policy aims to meet and set out audit procedures to confirm ongoing adherence.
Personnel Training and Accountability: Establish mandatory training for all staff on encryption basics, key handling procedures, and the disciplinary consequences for any failure to comply with the policy standards.
Creating a cryptography policy can feel like a big task. To help you get started, here’s a sample cryptography policy template that you can easily customise for your business.
Also Read: Understanding HR Audit: Purpose and Process
Building a policy from scratch can be time-consuming, diverting focus from your core business objectives. This practical breakdown of the essential sections will guide you in quickly drafting a comprehensive and actionable cryptography policy tailored to your company's specific needs and compliance obligations.
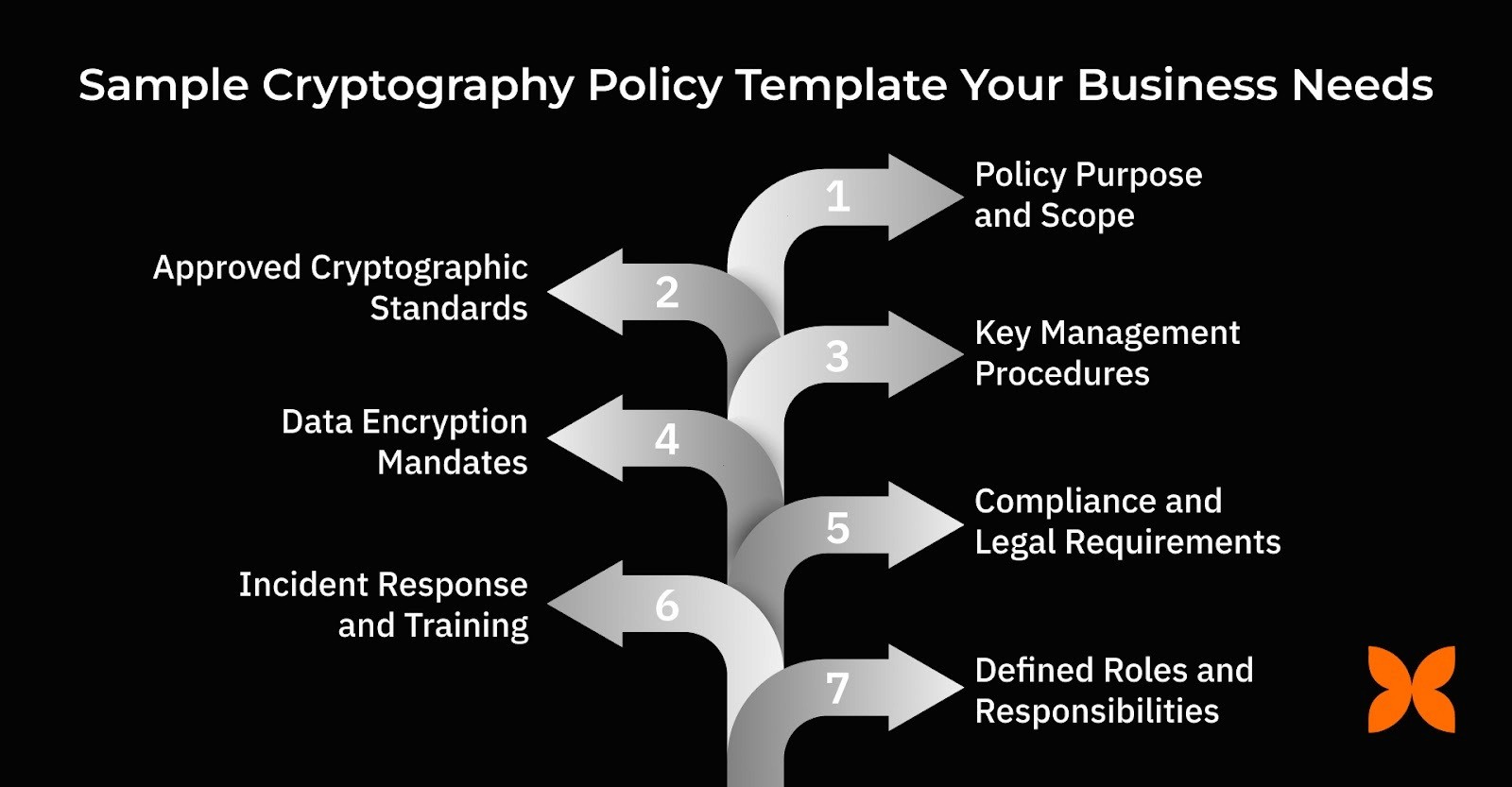
1.Policy Purpose and Scope
This section defines the 'why' and the 'what' of the policy, ensuring clarity on its mandatory nature and where its rules apply across the organisation.
Policy Purpose: State the policy's goal, which is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of all sensitive data through the consistent application of cryptographic controls.
Scope of Application: Clearly specify that the policy applies to all employees, contractors, systems, and processes that create, store, or transmit sensitive data.
Defining Sensitive Data: Explicitly list the types of information covered, such as customer Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial records, corporate Intellectual Property (IP), and internal strategy documents.
2.Approved Cryptographic Standards
To maintain a high and consistent level of protection, you must mandate specific, globally recognised security standards. Using outdated or weak standards leaves you vulnerable.
Symmetric Encryption: Mandate the use of AES-256 (Advanced Encryption Standard with a 256-bit key) for high-volume data encryption and storage.
Asymmetric Encryption: Specify RSA-2048 or higher, or equivalent modern standards like Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), for key exchange, digital signatures, and securing communications.
Hashing and Integrity: Require SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit) for verifying data integrity and securing passwords, forbidding the use of weaker methods like MD5 or SHA-1.
3.Key Management Procedures
Encryption keys are the secret keys to your data vault; if they are compromised, all your encryption is useless. This section details their secure handling across their entire lifespan.
Key Generation and Strength: Outline the requirement for keys to be generated using cryptographically secure methods and meet minimum length and randomness standards.
Secure Storage: Specify that all master and highly sensitive keys must be stored in secure, tamper-resistant environments, such as a Hardware Security Module (HSM) or a dedicated Cloud Key Management Service (KMS).
Key Rotation: Mandate a schedule for keys to be periodically retired and replaced with new, unique keys (e.g., every 90 days for certain operational keys) to limit the impact of a potential compromise.
Key Recovery and Disposal: Define a process for secure key backup and recovery in a disaster scenario, as well as a method for the irreversible, secure disposal of old or retired keys.
4.Data Encryption Mandates
This is the practical instruction set for protecting data wherever it resides or travels within and outside the organisation.
Data at Rest (Storage): Require encryption for all sensitive data stored on company servers, databases, cloud storage, and employee devices. Specify the use of full-disk encryption for laptops and secure database encryption for PII.
Data in Transit (Communication): Mandate the use of approved protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.2 or higher for all data transfer across public or internal networks, including website traffic, email, and API communications.
5.Compliance and Legal Requirements
Your policy must demonstrate a clear commitment to national and international data regulations, which is essential for audit purposes and preventing fines.
Regulatory Alignment: Directly reference relevant laws like the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, and how the policy's encryption requirements help meet legal obligations for data security.
Audit and Review: Establish a schedule for annual (or bi-annual) audits of cryptographic controls and key management systems, assigning clear accountability for compliance reporting.
6.Incident Response and Training
A policy is only effective if people are trained and processes are in place to handle emergencies.
Cryptographic Incident Response: Outline specific steps for the security team to follow if a cryptographic key is suspected of being compromised or if an encryption failure is detected.
Mandatory Awareness Training: Ensure all relevant staff receive compulsory, periodic training on their individual responsibilities related to encryption, proper password creation, and secure key handling.
7.Defined Roles and Responsibilities
This section assigns clear accountability for policy maintenance, enforcement, and daily operational security, ensuring no critical step is missed.
Information Security Team (CISO Office): Responsible for policy design, maintenance, and selection of all approved algorithms and protocols.
IT Operations and Engineering Teams: Accountable for the technical implementation (e.g., server configuration), day-to-day key management operations, and continuous monitoring of encryption systems.
All Employees and Contractors: Mandatory compliance with all policy standards, including encrypting sensitive data on personal devices and immediately reporting any key loss or security failure.
Executive Management: Responsible for final policy approval, resource allocation, and formal risk acceptance for any necessary exemptions.
To make your security efforts smooth, the next step is to get this comprehensive framework into an editable format.
Also Read: Understanding the Role and Responsibilities in HR Compliance
A formal policy is only as effective as its deployment. Successfully rolling out your new cryptography policy requires a disciplined, phased approach led by management, ensuring that technical integration and corporate accountability are established from day one.

This step-by-step guide helps employers ensure the policy translates from documentation into a mandatory, enforceable security practice:
Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Begin by formally auditing your current encryption landscape. Identify all sensitive data assets (PII, IP, financial records), classify their risk level, and pinpoint existing weaknesses in data handling, key management, and protocol use that the new policy must remediate.
Establish a Cross-Functional Steering Group: Form a mandatory task force responsible for overseeing the policy’s implementation and governance. This group must include senior representatives from Information Security, Legal/Compliance, IT Operations, and relevant Business Unit Heads to ensure buy-in and effective enforcement across all divisions.
Integrate Mandatory Technology Solutions: Deploy the approved cryptographic tools and systems into your infrastructure. This involves integrating secure Key Management Services (KMS) and ensuring that encryption-by-default is applied across all databases, cloud environments, and communication channels (TLS/SSL).
Define and Monitor Compliance Metrics: Establish clear, measurable success indicators for the policy. These metrics should focus on Compliance Rates (e.g., percentage of data encrypted, adherence to key rotation schedules) and be regularly reported to executive leadership to track progress and security posture.
Mandate Ongoing Training and Governance: Cryptography is not static. Implement compulsory, scheduled training for all staff based on their roles and responsibilities. Set up a periodic review cycle (at least annually) for the policy itself to ensure it remains aligned with evolving threats and the latest cryptographic standards.
With the implementation plan established, you are now prepared to enforce these crucial security measures.
Also Read: 10 Best HR Compliance Software in India for Small Businesses and Startups
Final Thoughts
Your data is your most valuable, yet most vulnerable, asset. A dedicated cryptography policy is your long-term insurance against crippling financial loss. It's not about installing more software; it’s about establishing clear, company-wide rules. By mandating strong encryption and rigorous key management, you protect your profits, uphold your legal duty, and secure your company’s ability to grow.
Security, in the digital age, is a competitive advantage. When customers and partners trust that your commitment to data secrecy is absolute, it builds confidence and enhances your reputation. Stop treating data protection as a tiresome chore and start seeing your policy as a business essential. Put the editable policy template to use today to make your data security an unbreakable foundation for success.
Disclaimer
The downloadable template and the information provided in this article are intended for general guidance and educational purposes only. They do not constitute legal advice or a legally binding document. Craze does not accept any responsibility or liability for any decisions made or actions taken based on this content. We recommend reviewing your final policy with legal or HR professionals before implementation.




